These findings are shared for research purposes and
indications for decision makers to help them broaden perspectives
and expand understanding until they materialize in a reviewed
paper.
Vitamin D, SUN, UVs
The epidemic took on a very different course between the northern and southern hemispheres. It picked up in late Fall/Aut
mn
until winter in Wuhan(Northern hemisphere) and Brazil (South
hemisphere). It then picked up in Europe and United States late
winter to subside as
spring arrived.
We
have
found that for a variety of European and Southern hemisphere cities,
there is strong association between daily UV levels (as published by
Tropospheric Emission Monitoring Internet Service
http://www.temis.nl/uvradiation/UVarchive/stations_uv.html
)
and deaths as well as new cases. The association is particularly strong when the lethality
and new cases are
lagged by 10-15 days (where the correlation coefficients range
between |0.2| and |0.6|) as shown in the charts below.
Amounts
of
sun needed may vary upon individual skin nature and pigmentation.
For
sunshine,
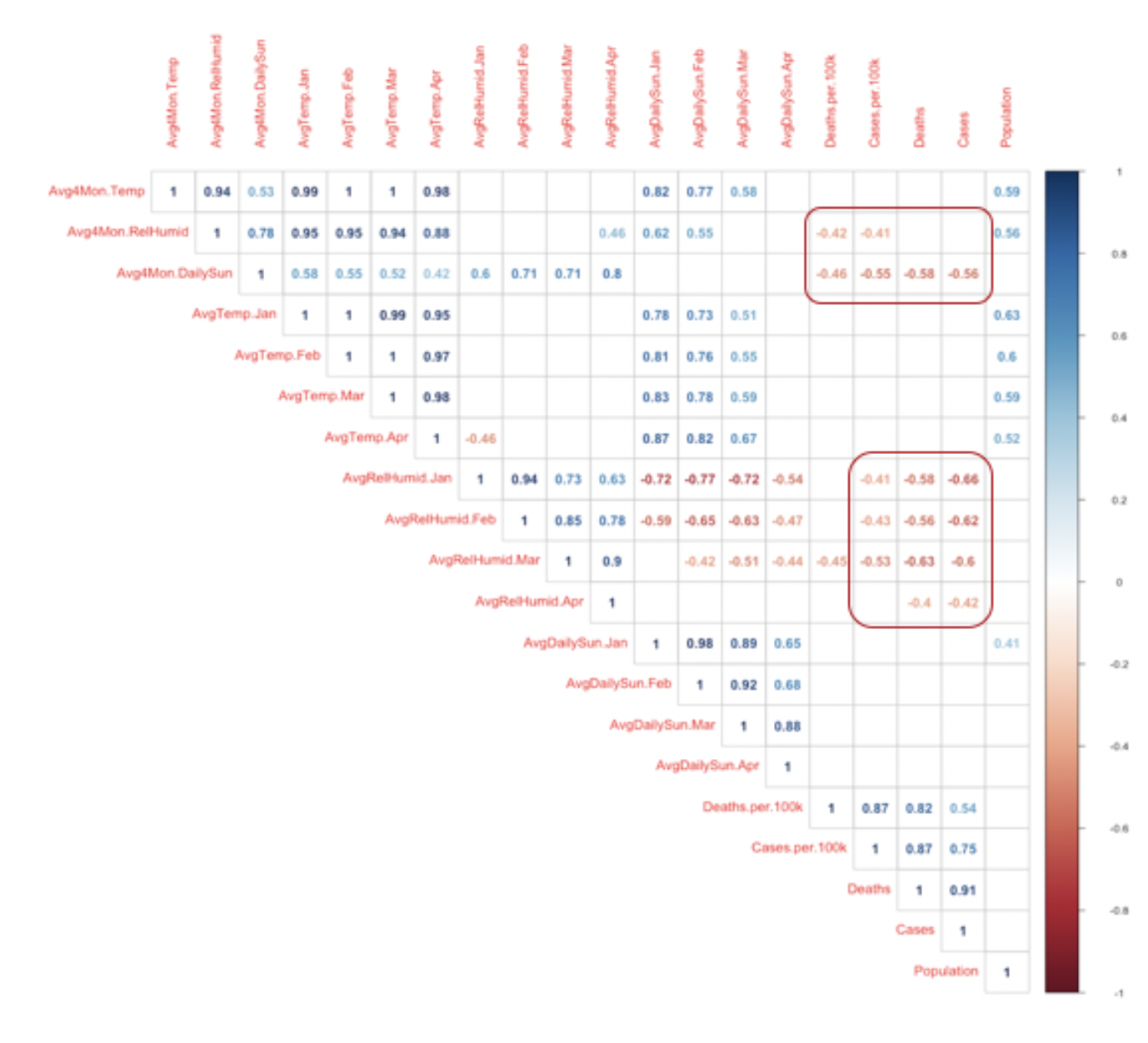
the 4-month average of daily sunshine is correlated with death per
capita, cases per capita, death count and case count at 0.1
significance level). There was no correlation for temperature.
Figure
2- Cross-Correlation of
UV index and Ozone for a selection of cities
Figure
3- Correlation matrix
of weather-related variables
Interestingly
enough,
at the time of writing this paper the epidemic is picking up in
middle east, India and Pakistan late spring in spite of very high UV
levels. This apparent contradiction may be explained by population
increasing use of air conditionning, avoiding sun and spending more
time in locked places thus creating better propagation conditions
and further explaining the need for sun and fresh air to reduce
spread or even reaching a point of disappearance.
The
south
to North gradient of epidemic curve drop in Europe as spring arrived
combined with lower peaks in countries where parks were open and
people accessing sun, further indicates a beneficial effect of sun
or uvs or light or vitamin D.
This
is further confirmed by the different studies made on vitamin D and
Covid.
F
Mitchell https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(20)30183-2/fulltext
V
Backman https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578v4
P
Ilie, S Stefanescu, L Smith https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-21211/v1
M
Ebadi, A J Montano-Loza https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-020-0661-0
M
Alipio https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Papers.cfm?abstract_id=3571484
It
has often been suggested that vitamin D may play a protective role
in many respiratory and inflammatory diseases. Such suggestion may
also be true for SARSCOV-2.
These
observations
significantly indicates a possible beneficial effect of sun exposure
on hosts beyond the direct effect UVs may have outdoor on the virus.
Figure
2 - Cross-Correlation of UV index and Ozone for cities
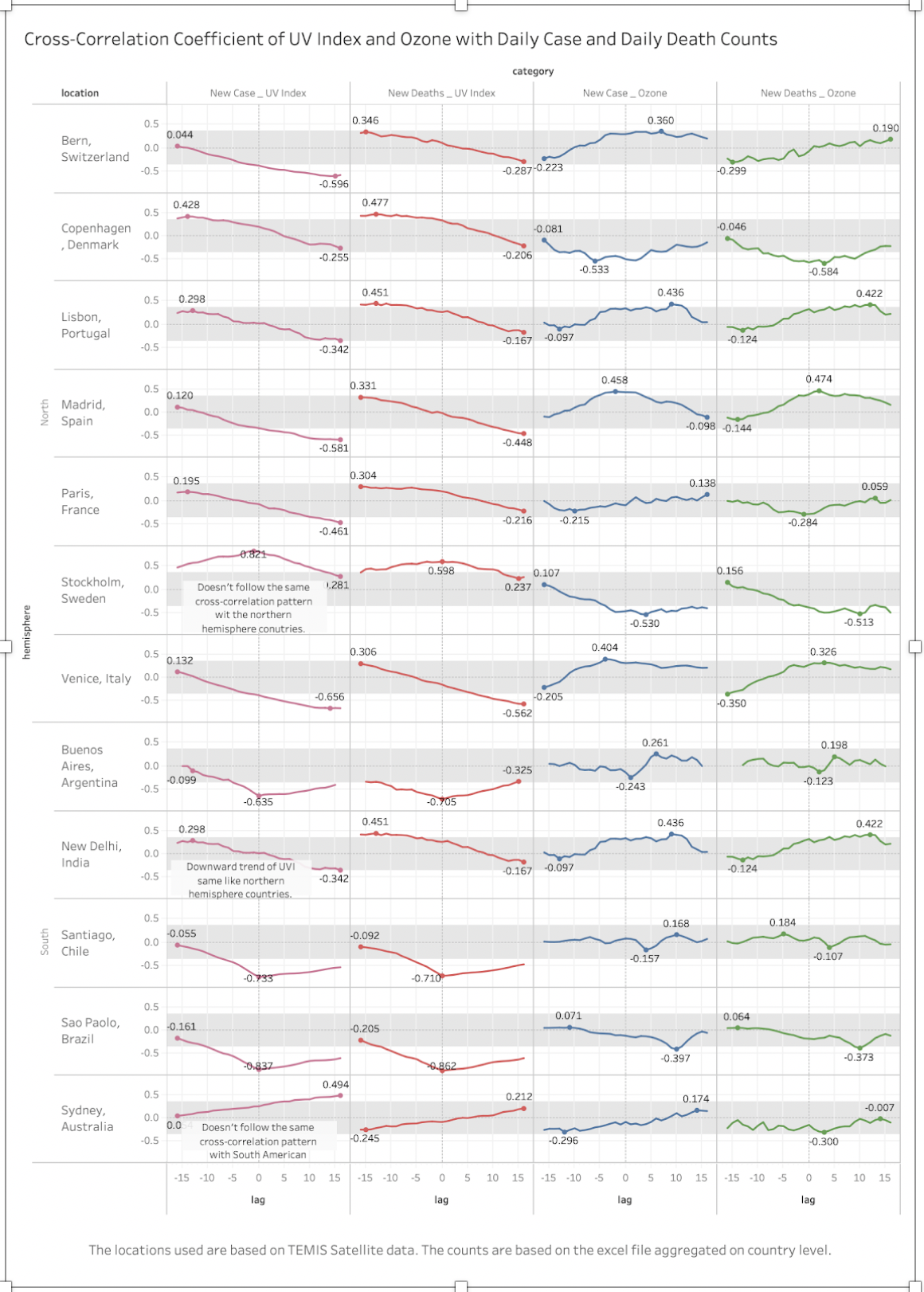
Figure 3 – Correlation matrix of weather-related
variables
(What cities or countries?)